Section 4.17 Worked Example: String methods
Subgoals for Calling a Method.
-
Write (instance / class) dot method name and ( )
-
Determine whether parameter(s) are appropriate
-
Number of parameters passed must match method declaration
-
Data types of parameters passed must be compatible with method declaration
-
-
Determine what the method will return and where it will be stored
-
Evaluate right hand side of assignment. Value is dependent on method’s purpose
Subsection 4.17.1 Problem Statement
Given the following code, determine the output.
String alpha = "alphabet";
String beta = "bet";
String gamma = "The cat in the hat.";
System.out.println(alpha.length());
System.out.println(alpha.indexOf(beta));
System.out.println(alpha.charAt(2));
System.out.println(gamma.toUpperCase());
String delta = gamma.substring(0,5);
System.out.println(delta);
delta = gamma.substring(8);
System.out.println(delta);
Subsection 4.17.2 SG1: Classify method as static method or instance method
String is a very versatile class in Java and is used to store 0 or more characters as a single entity. There are many different methods within the String class and this worked example will introduce you to some of the most commonly used. All methods used in this example are instance methods.
Subsection 4.17.3 SG2: Write (instance / class) dot method name and ( )
The methods called in this example are:
alpha.length();
alpha.indexOf(beta);
alpha.charAt(2);
gamma.toUpperCase();
gamma.substring(0,5);
gamma.substring(8);
Each method is called on a specific
String instance.
Subsection 4.17.4 SG3: Determine whether parameter(s) are appropriate
Some of the methods (
length, toUpper) have no parameters. indexOf requires one String parameter, charAt requires an integer parameter, substring requires one or two integers.
Subsection 4.17.5 SG4: Determine what the method will return and where it will be stored
Let’s evaluate this code by looking at the lines.
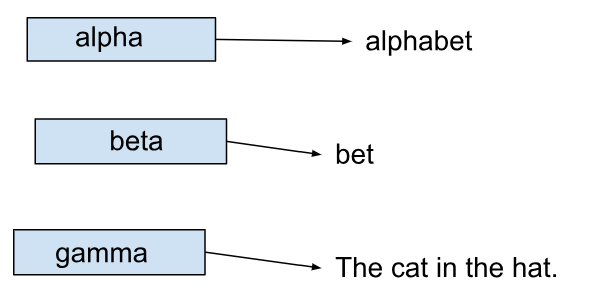
String alpha = "alphabet";
String beta = "bet";
String gamma = "The cat in the hat.";
These first 3 lines of code create 3
String objects:
System.out.println(alpha.length());
The length method returns the number of characters stored in the
String object. The string "alphabet" contains 8 characters, so the value 8 is printed.
System.out.println(alpha.indexOf(beta));
The
indexOf method searches the String object for the first occurrence of the parameter. In this case, we are looking for the value of beta ("bet") within alpha ("alphabet"). String characters have positions and the first character is at position 0.
| character | a | l | p | h | a | b | e | t |
| index | 0 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 |
The string "bet" begins at position 5 within "alphabet" so 5 is printed. If the string contained in
beta was not found within the string alpha, a -1 is returned.
System.out.println(alpha.charAt(2));
The
charAt method returns the character at the position indicated as the parameter. So this code would print the value at index 2, or ’p’.
System.out.println(gamma.toUpperCase());
The
toUpper method creates a new string that contains the upper case equivalent of all lower case characters. So calling the toUpper method on gamma ("The cat in the hat.") will create the string "THE CAT IN THE HAT." Any character that is not a lower case character is just copied directly into the new string. So this line would print "THE CAT IN THE HAT." (without the quotes). There is also a toLowerCase() method that creates a string with lower case characters.
Subsection 4.17.6 SG5: Evaluate right hand side (RHS) of assignment. Value is dependent on method’s purpose
Let’s evaluate the final code statements:
String delta = gamma.substring(0,5);
System.out.println(delta);
The
substring method creates a new string containing the characters at the first parameter position up to (but not including) the second parameter. So this code would take the first 5 characters (positions 0, 1, 2, 3, 4) of the string gamma ("The ") and assign it to the delta variable. The value "The " would be printed.
Notice that the integer parameters must be valid (the integer values cannot be negative, must be within the range of possible values, and the first parameter < second parameter).
delta = gamma.substring(8);
System.out.println(delta);
The version of the
substring method that takes one parameter, begins at that index and copies all the characters to the end of the string into a new string. So the characters beginning at position 8 "i" to the end will be assigned to delta. "in the hat." is printed.
Answer.
8
5
p
THE CAT IN THE HAT
The c
in the hat.
You have attempted of activities on this page.
