Skip to main content\(
\newcommand{\lt}{<}
\newcommand{\gt}{>}
\newcommand{\amp}{&}
\definecolor{fillinmathshade}{gray}{0.9}
\newcommand{\fillinmath}[1]{\mathchoice{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\displaystyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\textstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptstyle \phantom{\,#1\,}$}}{\colorbox{fillinmathshade}{$\scriptscriptstyle\phantom{\,#1\,}$}}}
\)
Section 7.3 Worked Example: For Loops - Counter
Subgoals for Evaluating a Loop.
-
-
Determine start condition
-
Determine update condition
-
Determine termination condition
-
Determine body that is repeated
-
-
For every iteration of loop, write down values
Subsection 7.3.1
You can watch this video or read through the content below it.
Problem: Given the following code, what is the output?
total = 0;
for (int x = 5; x < 50; x++)
{
if (x % 5 == 0)
total += x;
}
System.out.println(total);
Subsection 7.3.2 SG1: Diagram which statements go together.
Figure 7.3.1.
Subsection 7.3.3 SG2: Define and initialize variables
Figure 7.3.2.
Subsection 7.3.4 SG3: Trace the loop
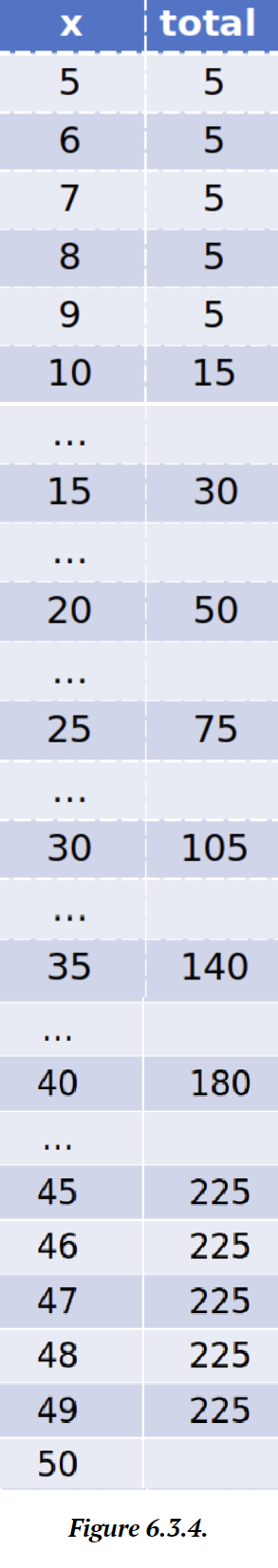
Figure 7.3.3.
Figure 7.3.4. X increments by 1, but the value is only added to total when it is evenly divisible by 5.
Notice that this example gives the equivalent
for loop for the
while loop in 6.1.
Answer.
You have attempted
of
activities on this page.