Section 4.10 Worked Example: Call a method of Random
Subgoals for Calling a Method.
-
Write (instance / class) dot method name and ( )
-
Determine whether parameter(s) are appropriate
-
Number of parameters passed must match method declaration
-
Data types of parameters passed must be compatible with method declaration
-
-
Determine what the method will return and where it will be stored
-
Evaluate right hand side of assignment. Value is dependent on method’s purpose
Subsection 4.10.1
You can watch this video or read through the content below it.
Subsection 4.10.2 Problem Statement
Given the following declaration and instantiation of a Random object, write the code to generate a random integer between 0 and 99.
Random rand = new Random();
Subsection 4.10.3 SG1: Classify method as static method or instance method
We already have an instance of Random with the variable name
rand.
First, check the API to find a method that does what we want.
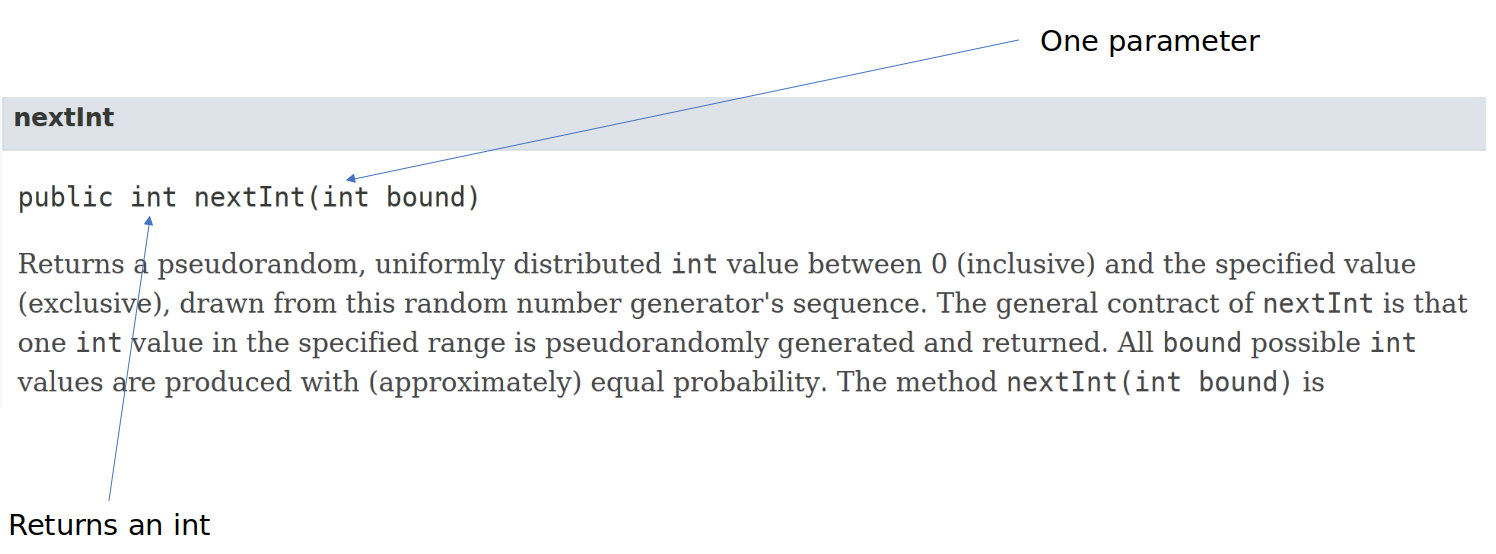
In looking at the documentation for the Random class, we see the
nextInt() method does not contain the keyword static, so we can assume that it is an instance method. Because we want to call an instance method, we need to identify the instance which will call the method. In this example we have already created a Random instance which is named rand.
Subsection 4.10.4 SG2: Write (instance / class) dot method name and ( )
Here is the method call with the instance:
rand.nextInt()
Subsection 4.10.5 SG3: Determine whether parameter(s) are appropriate
According to the API documentation, the
nextInt method requires 1 parameter, the exclusive upper bound. If we want to generate random values between 0 to 99 (inclusive) then parameter will be 100.
rand.nextInt(100)
To shift the starting value from 0 for the random number values, you simply add that value after generation of the random number.
rand.nextInt(100) + 100;
This will create values in the range from 100 to 199, since
rand.next(100) yields values from 0 to 99.
Subsection 4.10.6 SG4: Determine what the method will return and where it will be stored
According to the API documentation, the
nextInt method returns an integer, so we need an int type variable to store the value.
int value = input.nextInt();
Subsection 4.10.7 SG5: Evaluate right hand side (RHS) of assignment. Value is dependent on method’s purpose
The
nextInt method generates an integer value and returns it. So the RHS is an integer and the LHS is an integer variable, so the assignment statement is valid.
int value = input.nextInt();
Practice Pages.
You have attempted of activities on this page.
