Activity 9.3.1.
What does this code print out? Trace through the code with the Show CodeLens button. Notice how the this Pay object is passed to the Overtime constructor.
this as an Argument
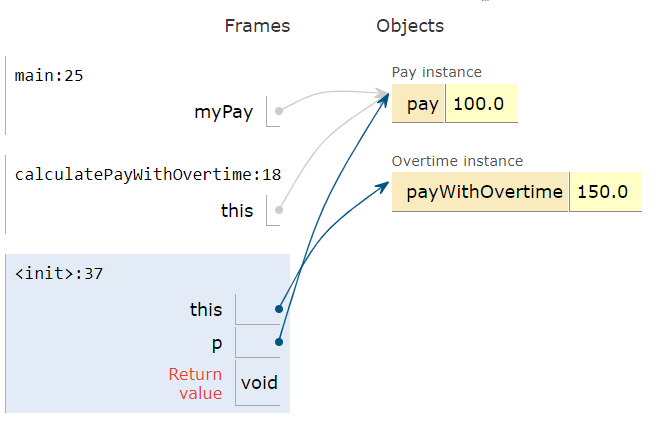
this variable can be used anywhere you would use an object variable. You can even pass it to another method as an argument. Consider the classes below, Pay and Overtime. The Pay class declares an Overtime object and passes in this (the current Pay object) to its constructor which computes the overtime with respect to that Pay object. Try this code in the active code exercise below with the Show CodeLens button to trace through it step by step. Here is an image that shows how this, myPay and p all refer to the same object in memory.
public class Pay {
private double pay;
public Pay(double p) {
pay = p;
}
public double getPay() {
return pay;
}
public void calculatePayWithOvertime() {
// this Pay object is passed to the Overtime constructor
Overtime ot = new Overtime(this);
pay = ot.getOvertimePay();
}
}
public class Overtime {
private double payWithOvertime;
public Overtime(Pay p) {
payWithOvertime = p.getPay() * 1.5;
}
public double getOvertimePay() {
return payWithOvertime;
}
}
Pay one = new Pay(20.0);
one.calculatePayWithOvertime();
System.out.println(one.getPay());

www.youtube.com/watch?v=YpD1tJK9vIA&ab_channel=Doyouknow%3Fthis keyword to distinguish between the instance variables and the parameter variables.
withdraw(amount) and deposit(amount) methods for the class. The withdraw method should subtract the amount from the balance as long as there is enough money in the account (the balance is larger than the amount). And deposit should add the amount to the balance. Use the this keyword to refer to the balance.
main method that creates a BankAccount object and calls its deposit and withdraw methods and prints out the object to test its toString method.
this (one constructor to initialize all 3 instance variables and one that only has 2 parameters for the name and account number and initializes the balance to 0), a toString() method, and withdraw(amount) and deposit(amount) methods. Test your class in a main method.
this acts as a special variable that holds a reference to the current object—the object whose method or constructor is being called.
this.instanceVariable can be used to distinguish between this object’s instance variables and local parameter variables that may have the same variable names.
this can be used to pass the current object as an argument in a method call.
this reference.
public class Liquid {
private int currentTemp;
public Liquid(int ct) {
currentTemp = ct;
}
public int getCurrentTemp() {
return currentTemp;
}
public void addToJar(LiquidJar j) {
j.addLiquid(this);
}
}
public class LiquidJar {
private int totalTemp;
public LiquidJar() {
totalTemp = 0;
}
public void addLiquid(Liquid l) {
totalTemp += l.getCurrentTemp();
}
public int getTotalTemp() {
return totalTemp;
}
// Constructor not shown.
}
Liquid water = new Liquid(50);
Liquid milk = new Liquid(15);
LiquidJar j = new LiquidJar();
water.addToJar(j);
milk.addToJar(j);
System.out.println(j.getTotalTemp());