Activity 10.3.1.
The following code will throw an
IndexOutOfBoundsException. Can you fix it?
ArrayList traversals
ArrayList when we use a loop to access its elements in order. Traversing an ArrayList is very similar to traversing an array; we use the same kinds of loops and just have to swap the length property of arrays for the size() method of ArrayList and use get and set methods instead of array access expressions with [].
ArrayList. Additionally we can write algorithms that remove elements from an ArrayList while we loop over it though as we’ll see we do need to exercise some care.
for loop over an ArrayList
for loop that runs n times:
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// whatever
}
n with array.legnth and in the body of the loop used array[i] to access the individual elements of the array.
for (int i = 0; i < array.length; i++) {
// whatever with array[i]
}
ArrayList using list.size() in the loop condition list.get(i) and list.set(i, value) in the body of the loop to access the individual elements of the ArrayList.
for (int i = 0; i < list.size(); i++) {
// whatever with list.get(i) and list.set(i, value)
}
ArrayList can grow and shrink via the add and remove methods, the get and set methods still require a valid index, i.e. greater than or equal to 0 and less than the size of the ArrayList. So if we try to use an index that is outside that range, the code will throw an IndexOutOfBoundsException, similar to the ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException thrown if we use an invalid index in an array access expression..
IndexOutOfBoundsException. Can you fix it?
for loop
for loop to traverse all of the items in an ArrayList when we only care about the values in the list and not their indexes. The type of the loop variable needs to be the same as the type parameter of the ArrayList but if the type parameter is a wrapper class like Integer we can (and usually should) use the primitive type for the loop variable and let auto-unboxing take care of it for us.
ArrayList<String> strings = new ArrayList<>();
ArrayList<Integer> numbers = new ArrayList<>();
// Loop variable is a String, the element type of strings
for (String s : strings) {
// do stuff with s
}
// Loop variable is an int, the unboxed version of the element type
for (int n : numbers) {
// do stuff with n
}
// Less stylish but this also works. n will probably be unboxed as needed in the body
for (Integer n : numbers) {
// do stuff with n
}
numbers by multiplying them. Print out the product after the new loop.
for loop is that we can’t add or remove items from an ArrayList while we loop over it. We’ll see in a later section how to write loops that remove items from an ArrayList using a regular for loop, but with an enhanced for loop if the size of an ArrayList changes in any way, such as by a call to add or remove, while it is being looped over, the loop will immediately throw a ConcurrentModificationException.
ArrayList can be a regular class that we could have written ourselves yet it can be used with the special enhanced for loop syntax. The full resolution to that mystery is well beyond the scope of the AP curriculum but it happens that the way the enhanced for loop is defined in terms of an interface that any class can implement and ArrayList is one of the classes that does. So if you wanted to write your own class that you could loop over with an enhanced for loop, you could.
while loop
while loop to traverse an ArrayList. If we want to go element by element we’ll have to manage an index variable separately at which point a for loop might make more sense, but if we want to repeatedly modify an ArrayList until some condition is met a while loop can be just the thing. For example this code uses a while loop to remove all the elements from the beginning of an ArrayList, numbers, that are less than 100.
// numbers is an ArrayList<Integer>
// Loop as long as there are elements in teh list and element 0 is < 100
while (numbers.size() > 0 && numbers.get(0) < 100) {
// Remove element 0
numbers.remove(0);
}
numbers is either empty or starts with a number greater than or equal to 100. There may be numbers less than 100 later in the list but all the ones at the start will have been removed.
while loop and an object-oriented approach where the list is a field of the current object and an instance method rather than a class (static) method loops through the list.
nums has been created as an ArrayList object and it initially contains the following Integer values [0, 0, 4, 2, 5, 0, 3, 0]. What will nums contain as a result of executing numQuest?
ArrayList<Integer> list1 = new ArrayList<>();
private ArrayList<Integer> nums;
// precondition: nums.size() > 0;
// nums contains Integer objects
public void numQuest()
{
int k = 0;
Integer zero = new Integer(0);
while (k < nums.size())
{
if (nums.get(k).equals(zero))
nums.remove(k);
k++;
}
}
ArrayList. For example, here is an ArrayList of Students. Let’s write some loops that traverse the ArrayList to print out each Student by implicitly calling its toString() method. We’ll also write a method that filters the ArrayList to print out only the students who have a GPA higher than 3.5 for the honor roll.
// get the name of the 0's student
String name = students.get(0).getName();
// get the GPA of the student at index i
double gpa = students.get(i).getGPA();
WordPair that can store pairs of words.
class WordPair
{
private String word1;
private String word2;
public WordPair(String word1, String word2)
{
this.word1 = word1;
this.word2 = word2;
}
public String getFirst()
{
return word1;
}
public String getSecond()
{
return word2;
}
public String toString()
{
return "(" + word1 + ", " + word2 + ")";
}
}
ArrayList of WordPair objects below. Look at the StudentList example above for help.
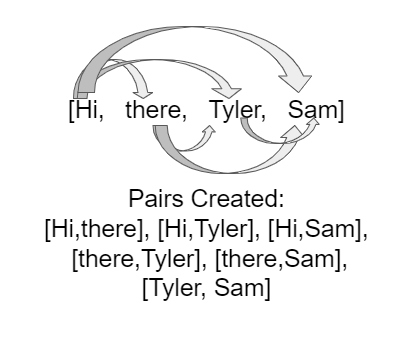
WordPairsList below, you will write the constructor which takes the array of words and pairs them up as shown in the figure. You will need nested loops to pair each element with the rest of the elements in the list.
words array for the first word in the word pair (for loop from index i = 0 to length-1)
i + 1 for the second word in the word pair (for loop from index j = i + 1 to length)
WordPairsList below which will add pairs of words from a given array to the ArrayList. Then, complete the method numMatches() as described below this exercise.
numMatches that counts and returns the number of pairs where the first word is the same as the second word. For example, if the word array is ["hi","bye","hi"], the pairs generated would be ["hi","bye"], ["hi","hi"], and ["bye","hi"]. In the second pair ["hi","hi"], the first word is the same as the second word, so numMatches would return 1.
ArrayList allPairs and for each WordPair in allPairs, it checks to see if its first word (using the getFirst method) equals the second word (using the getSecond method). If there is a match, it increments a counter which it returns at the end of the method. To test this method, add another “there” into the words array and then uncomment the call to numMatches.
ArrayList is when iteration or recursive statements are used to access all or an ordered sequence of the elements in an ArrayList.
ArrayLists can be traversed with an enhanced for loop, a while loop, or a regular for loop using an index.
ArrayList requires the use of special techniques to avoid skipping elements (since remove moves all the elements above the removed index down.)
IndexOutOfBoundsException. (The indices for an ArrayList start at 0 and end at the number of elements − 1).
ArrayList while traversing it using an enhanced for loop can result in a ConcurrentModificationException. Therefore, when using an enhanced for loop to traverse an ArrayList, you should not add or remove elements.