Section 1.8 Getting Started with Data
We stated above that Python supports the object-oriented programming paradigm. This means that Python considers data to be the focal point of the problem-solving process. In Python, as well as in any other object-oriented programming language, we define a class to be a description of what the data look like (the state) and what the data can do (the behavior). Classes are analogous to abstract data types because a user of a class only sees the state and behavior of a data item. Data items are called objects in the object-oriented paradigm. An object is an instance of a class.
Subsection 1.8.1 Built-in Atomic Data Types
We will begin our review by considering the atomic data types. Python has two main built-in numeric classes that implement the integer and floating-point data types. These Python classes are called
int and float. The standard arithmetic operators, +, -, *, /, and ** (exponentiation), can be used with parentheses forcing the order of operations away from normal operator precedence. Other very useful operators are the remainder (modulo) operator (%) and integer division (//). Note that when two integers are divided, the result is a floating point. The integer division operator returns the integer portion of the quotient by truncating any fractional part.
The Boolean data type, implemented as the Python
bool class, will be quite useful for representing truth values. The possible state values for a Boolean object are True and False with the standard Boolean operators, and, or, and not.
>>> True True >>> False False >>> False or True True >>> not (False or True) False >>> True and True True
Boolean data objects are also used as results for comparison operators such as equality (==) and greater than (
| Operation Name | Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| less than | Less than operator | |
| greater than | Greater than operator | |
| less than or equal | Less than or equal to operator | |
| greater than or equal | Greater than or equal to operator | |
| equal | Equality operator | |
| not equal | Not equal operator | |
| logical and | Both operands True for result to be True | |
| logical or | One or the other operand is True for the result to be True | |
| logical not | Negates the truth value, False becomes True, True becomes False |
Identifiers are used in programming languages as names. In Python, identifiers start with a letter or an underscore (_), are case sensitive, and can be of any length. Remember that it is always a good idea to use names that convey meaning so that your program code is easier to read and understand.
A Python variable is created when a name is used for the first time on the left-hand side of an assignment statement. Assignment statements provide a way to associate a name with a value. The variable will hold a reference to a piece of data but not the data itself. Consider the following session:
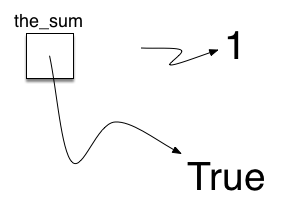
>>> the_sum = 0 >>> the_sum 0 >>> the_sum = the_sum + 1 >>> the_sum 1 >>> the_sum = True >>> the_sum True
The assignment statement
the_sum = 0 creates a variable called the_sum and lets it hold the reference to the data object 0 (see Figure 1.8.2). In general, the right-hand side of the assignment statement is evaluated and a reference to the resulting data object is assigned to the name on the left-hand side. At this point in our example, the type of the variable is integer as that is the type of the data currently being referred to by the_sum. If the type of the data changes (see Figure 1.8.3), as shown above with the Boolean value True, so does the type of the variable (the_sum is now of the type Boolean). The assignment statement changes the reference being held by the variable. This is a dynamic characteristic of Python. The same variable can refer to many different types of data.

Subsection 1.8.2 Built-in Collection Data Types
In addition to the numeric and Boolean classes, Python has a number of very powerful built-in collection classes. Lists, strings, and tuples are ordered collections that are very similar in general structure but have specific differences that must be understood for them to be used properly. Sets and dictionaries are unordered collections.
A list is an ordered collection of zero or more references to Python data objects. Lists are written as comma-delimited values enclosed in square brackets. The empty list is simply
[ ]. Lists are heterogeneous, meaning that the data objects need not all be from the same class and the collection can be assigned to a variable as below. The following fragment shows a variety of Python data objects in a list.
>>> [1, 3, True, 6.5] [1, 3, True, 6.5] >>> my_list = [1, 3, True, 6.5] >>> my_list [1, 3, True, 6.5]
Note that when Python evaluates a list, the list itself is returned. However, in order to remember the list for later processing, its reference needs to be assigned to a variable.
Since lists are considered to be sequentially ordered, they support a number of operations that can be applied to any Python sequence. Table 1.8.4 reviews these operations and the following session gives examples of their use.
| Operation Name | Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| indexing | [ ] | Access an element of a sequence |
| concatenation | + | Combine sequences together |
| repetition | * | Concatenate a repeated number of times |
| membership | in | Ask whether an item is in a sequence |
| length | len | Ask the number of items in the sequence |
| slicing | [ : ] | Extract a part of a sequence |
Note that the indices for lists (sequences) start counting with 0. The slice operation my_list[1:3] returns a list of items starting with the item indexed by 1 up to—but not including—the item indexed by 3.
Sometimes you will want to initialize a list. This can quickly be accomplished by using repetition. For example,
>>> my_list = [0] * 6 >>> my_list [0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0]
One very important aside relating to the repetition operator is that the result is a repetition of references to the data objects in the sequence. This can best be seen by considering the following session:
The variable
big_list holds a collection of three references to the original list called my_list. Note that a change to one element of my_list shows up in all three occurrences in big_list.
Lists support a number of methods that will be used to build data structures. Table 1.8.5 provides a summary. Examples of their use follow.
| Method Name | Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
append |
a_list.append(item) |
Adds a new item to the end of a list |
insert |
a_list.insert(i,item) |
Inserts an item at the ith position in a list |
pop |
a_list.pop() |
Removes and returns the last item in a list |
pop |
a_list.pop(i) |
Removes and returns the ith item in a list |
sort |
a_list.sort() |
Sorts a list in place |
reverse |
a_list.reverse() |
Modifies a list to be in reverse order |
del |
del a_list[i] |
Deletes the item in the ith position |
index |
a_list.index(item) |
Returns the index of the first occurrence of item
|
count |
a_list.count(item) |
Returns the number of occurrences of item
|
remove |
a_list.remove(item) |
Removes the first occurrence of item
|
You can see that some of the methods, such as
pop, return a value and also modify the list. Others, such as reverse, simply modify the list with no return value. pop will default to the end of the list but can also remove and return a specific item. The index range starting from 0 is again used for these methods. You should also notice the familiar “dot” notation for asking an object to invoke a method. my_list.append(False) can be read as “ask the object my_list to perform its append method and send it the value False.” Even simple data objects such as integers can invoke methods in this way.
>>> (54).__add__(21) 75
In this fragment we are asking the integer object
54 to execute its add method (called __add__ in Python) and passing it 21 as the value to add. The result is the sum, 75. Of course, we usually write this as 54+21. We will say much more about these methods later in this section.
One common Python function that is often discussed in conjunction with lists is the
range function. range produces a range object that represents a sequence of values. By using the list function, it is possible to see the value of the range object as a list. This is illustrated below.
>>> range(10) range(0, 10) >>> list(range(10)) [0, 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> range(5, 10) range(5, 10) >>> list(range(5, 10)) [5, 6, 7, 8, 9] >>> list(range(5, 10, 2)) [5, 7, 9] >>> list(range(10, 1, -1)) [10, 9, 8, 7, 6, 5, 4, 3, 2]
The range object represents a sequence of integers. By default, it will start with 0. If you provide more parameters, it will start and end at particular points and can even skip items. In our first example,
range(10), the sequence starts with 0 and goes up to but does not include 10. In our second example, range(5, 10) starts at 5 and goes up to but does not include 10. range(5, 10, 2) performs similarly but skips by twos (again, 10 is not included).
Strings are sequential collections of zero or more letters, numbers, and other symbols. We call these letters, numbers, and other symbols characters. Literal string values are differentiated from identifiers by using quotation marks (either single or double).
>>> "David" 'David' >>> my_name = "David" >>> my_name[3] 'i' >>> my_name * 2 'DavidDavid' >>> len(my_name) 5
Since strings are sequences, all of the sequence operations described above work as you would expect. In addition, strings have a number of methods, some of which are shown in Table 1.8.6.
| Method Name | Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
center |
a_string.center(w) |
Returns a string centered in a field of size w
|
count |
a_string.count(item) |
Returns the number of occurrences of item in the string |
ljust |
a_string.ljust(w) |
Returns a string left-justified in a field of size w
|
lower |
a_string.lower() |
Returns a string in all lowercase |
rjust |
a_string.rjust(w) |
Returns a string right-justified in a field of size w
|
find |
a_string.find(item) |
Returns the index of the first occurrence of item
|
split |
a_string.split(s_char) |
Splits a string into substrings at s_char
|
Of these,
split will be very useful for processing data. split will take a string and return a list of strings using the split character as a division point. In the example below, “v” is the division point. If no division is specified, the split method looks for whitespace characters such as tab, newline, and space.
>>> my_name
'David'
>>> my_name.upper()
'DAVID'
>>> my_name.center(10)
' David '
>>> my_name.find("v")
2
>>> my_name.split("v")
['Da', 'id']
A major difference between lists and strings is that lists can be modified while strings cannot. This is referred to as mutability. Lists are mutable; strings are immutable. For example, you can change an item in a list by using indexing and assignment. With a string that change is not allowed, as shown below.
>>> my_list [1, 3, True, 6.5] >>> my_list[0] = 2 ** 10 >>> my_list [1024, 3, True, 6.5] >>> >>> my_name 'David' >>> my_name[0] = "X" Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: 'str' object does not support item assignment
Tuples are very similar to lists in that they are heterogeneous sequences of data. The difference is that a tuple is immutable, like a string. A tuple cannot be changed. Tuples are written as comma-delimited values enclosed in parentheses. As sequences, they can use any operation described above. For example,
>>> my_tuple = (2, True, 4.96) >>> my_tuple (2, True, 4.96) >>> len(my_tuple) 3 >>> my_tuple[0] 2 >>> my_tuple * 3 (2, True, 4.96, 2, True, 4.96, 2, True, 4.96) >>> my_tuple[0:2] (2, True)
However, if you try to change an item in a tuple, you will get an error. Note that the error message provides the location and reason for the problem.
>>> my_tuple[1] = False Traceback (most recent call last): File "<stdin>", line 1, in <module> TypeError: 'tuple' object does not support item assignment
A set is an unordered collection of zero or more immutable Python data objects. Sets do not allow duplicates and are written as comma-delimited values enclosed in curly braces. The empty set is represented by
set(). Sets are heterogeneous, and the collection can be assigned to a variable as below.
>>> {3, 6, "cat", 4.5, False}
{False, 3, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
>>> my_set = {3, 6, "cat", 4.5, False}
>>> my_set
{False, 3, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
Even though sets are not considered to be sequential, they do support a few of the familiar operations presented earlier. Table 1.8.7 reviews these operations and the following session gives examples of their use.
| Operation Name | Operator | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
| membership | in |
Set membership |
| length | len |
Returns the cardinality of the set |
| |
a_set | other_set |
Returns a new set with all elements from both sets |
& |
a_set & other_set |
Returns a new set with only those elements common to both sets |
- |
a_set - other_set |
Returns a new set with all items from the first set not in the second |
<= |
a_set <= other_set |
Asks whether all elements of the first set are in the second |
>>> my_set
{False, 3, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
>>> len(my_set)
5
>>> False in my_set
True
>>> "dog" in my_set
False
Sets support a number of methods that should be familiar to those who have worked with them in a mathematics setting. Table 1.8.8 provides a summary. Examples of their use follow. Note that
union, intersection, issubset, and difference all have operators that can be used as well.
| Method Name | Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
union |
a_set.union(other_set) |
Returns a new set with all elements from both sets |
intersection |
a_set.intersection(other_set) |
Returns a new set with only those elements common to both sets |
difference |
a_set.difference(other_set) |
Returns a new set with all items from the first set not in the second |
issubset |
a_set.issubset(othe_rset) |
Asks whether all elements of one set are in the other |
add |
a_set.add(item) |
Adds item to the set |
remove |
a_set.remove(item) |
Removes item from the set |
pop |
a_set.pop() |
Removes an arbitrary element from the set |
clear |
a_set.clear() |
Removes all elements from the set |
>>> my_set
{False, 3, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
>>> your_set = {99, 3, 100}
>>> my_set.union(your_set)
{False, 3, 4.5, 'cat', 6, 99, 100}
>>> my_set | your_set
{False, 3, 4.5, 'cat', 6, 99, 100}
>>> my_set.intersection(your_set)
{3}
>>> my_set & your_set
{3}
>>> my_set.difference(your_set)
{False, 'cat', 4.5, 6}
>>> my_set - your_set
{False, 'cat', 4.5, 6}
>>> {3, 100}.issubset(your_set)
True
>>> {3, 100} <= your_set
True
>>> my_set.add("house")
>>> my_set
{False, 'house', 3, 4.5, 6, 'cat'}
>>> my_set.remove(4.5)
>>> my_set
{False, 'house', 3, 6, 'cat'}
>>> my_set.pop()
False
>>> my_set
{'house', 3, 6, 'cat'}
>>> my_set.clear()
>>> my_set
set()
Our final Python collection is an unordered structure called a dictionary. Dictionaries are collections of associated pairs of items where each pair consists of a key and a value. This key-value pair is typically written as key:value. Dictionaries are written as comma-delimited key:value pairs enclosed in curly braces. For example,
>>> capitals = {"Iowa": "Des Moines", "Wisconsin": "Madison"}
>>> capitals
{'Iowa': 'Des Moines', 'Wisconsin': 'Madison'}
We can manipulate a dictionary by accessing a value via its key or by adding another key-value pair. The syntax for access looks much like a sequence access except that instead of using the index of the item, we use the key value. To add a new value is similar.
It is important to note that prior to Python 3.6 dictionaries were maintained in no particular order with respect to the keys. The first pair added (
"Utah": "Salt Lake City") would be placed first in the dictionary and the second pair added ("California": "Sacramento") would be placed last. The placement of a key is dependent on the idea of hashing, which will be explained in more detail in Chapter 5. Dictionaries do maintain the order since Python 3.6, so in the example above the pairs appear in the dictionary in the order they were added. We also show the length function performing the same role as with other collections.
Dictionaries have both methods and operators. Table 1.8.9 and Table 1.8.10 describe them, and the session shows them in action. The
keys, values, and items methods all return objects that contain the values of interest. You can use the list function to convert them to lists. You will also see that there are two variations on the get method. If the key is not present in the dictionary, get will return None. However, a second, optional parameter can specify a return value instead.
| Operator | Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
[] |
a_dict[k] |
Returns the value associated with k, otherwise its an error |
in |
key in a_dict |
Returns True if key is in the dictionary, False otherwise |
del |
del a_dict[key]
|
Removes the entry from the dictionary |
| Method Name | Use | Explanation |
|---|---|---|
keys |
a_dict.keys() |
Returns the keys of the dictionary in a dict_keys object |
values |
a_dict.values() |
Returns the values of the dictionary in a dict_values object |
items |
a_dict.items() |
Returns the key-value pairs in a dict_items object |
get |
a_dict.get(k) |
Returns the value associated with k, None otherwise |
get |
a_dict.get(k, alt) |
Returns the value associated with k, alt otherwise |
>>> phone_ext={"david": 1410, "brad": 1137, "roman": 1171}
>>> phone_ext
{'david': 1410, 'brad': 1137, 'roman': 1171}
>>> phone_ext.keys()
dict_keys(['david', 'brad', 'roman'])
>>> list(phone_ext.keys())
['david', 'brad', 'roman']
>>> phone_ext.values()
dict_values([1410, 1137, 1171])
>>> list(phone_ext.values())
[1410, 1137, 1171]
>>> phone_ext.items()
dict_items([('david', 1410), ('brad', 1137), ('roman', 1171)])
>>> list(phone_ext.items())
[('david', 1410), ('brad', 1137), ('roman', 1171)]
>>> phone_ext.get("kent")
>>> phone_ext.get("kent", "NO ENTRY")
'NO ENTRY'
You have attempted 1 of 6 activities on this page.

