10.2. Accessing elements¶
The [] operator reads and writes the elements of a vector in much
the same way it accesses the characters in an string. This is called
vector indexing. As with strings, the indices start at zero, so count[0]
refers to the “zeroeth” element of the vector, and count[1] refers to the
“oneth” element. You can use the [] operator anywhere in an expression:
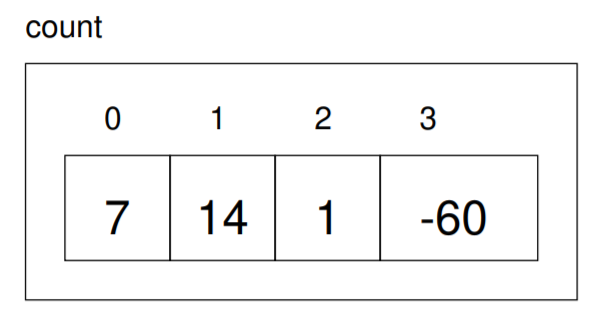
count[0] = 7;
count[1] = count[0] * 2;
count[2]++;
count[3] -= 60;
All of these are legal assignment statements. Here is the effect of this code fragment:
Warning
Since elements of this vector are numbered from 0 to 3, there is no element with the index 4. It is a common error to go beyond the bounds of a vector, which causes a run-time error. The program outputs an error message like “Illegal vector index”, and then quits.
You can use any expression as an index, as long as it has type int.
One of the most common ways to index a vector is with a loop variable.
For example:
int i = 0;
while (i < 4) {
cout << count[i] << endl;
i++;
}
This while loop counts from 0 to 4; when the loop variable i is
4, the condition fails and the loop terminates. Thus, the body of the
loop is only executed when i is 0, 1, 2 and 3.
Each time through the loop we use i as an index into the vector,
outputting the ith element. This type of vector traversal is very
common. Vectors and loops go together like fava beans and a nice
Chianti.
Take a look at the active code below. We can modify the vectors by accessing its elements.
vec[3] = vec[3]++;-
Incorrect! This is actually incrementing the 4th element of vec, since vectors are zero indexed.
vec(3) = vec(3) + 1;-
Incorrect! This is not proper syntax.
vec[2]++;-
vec[2]is the third element and we increment it by using the++operator. vec(2) = vec(2)++;-
This is not proper syntax.
vec[2] = vec[2] + 1-
vec[2]is the third element and we increment it by adding 1.
Q-2: Multiple Response How would you increment the third element of vector<int> vec by one?