3.7. Comparing Objects¶
Comparing objects is a little different than comparing primitive typed values like numbers. Objects can be very complex and have many attribute values or instance variables inside them. For example, the Turtle objects have many instance variables like name, width, height, xPos, yPos, etc. When comparing two Turtle objects, we need a specially written equals method to compare all of these values. In this lesson, we will take a look at String objects and the difference between comparing them with == vs. the equals method.
3.7.1. String Equality¶
The equals method for Strings compares two strings letter by letter. s1.equals(s2) is true if s1 and s2 have all the same characters in the same order. With Strings and other objects, you almost always use equals instead of == to check their equality.
When the operator == is used to compare object variables, it returns true when the two variables refer to the same object. These variables are called object references and aliases for the same object. With strings this happens when one string variable is set to another.
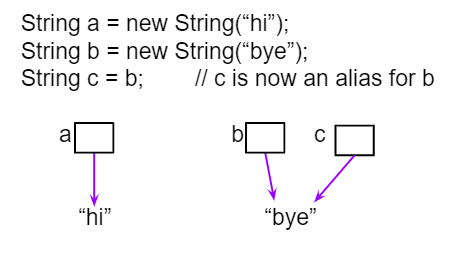
Figure 1: String aliases¶
If you run the following, what will be printed?
The following video traces through the code above and shows how == and equals work with String objects in memory.
Here’s the representation of memory where s2 and s3 refer to the same String object.

Figure 2: s2 and s3 are aliases referring to the same String object¶
3.7.2. Equality with New Strings¶
If you use the new keyword to create a string, it will always create a new string object. So, even if we create two string objects with new that contain all the same characters in the same order, they will not refer to the same object.
What will the following print?
Watch the video below to see how this code works in memory. Since we used the new keyword, two different String objects will be created that each have the characters Hello in them. So s1 == s2 will be false since they don’t refer to the same object, but s1.equals(s2) is true since the two different objects contain the same characters in the same order.
Here is the representation of these String objects in memory.
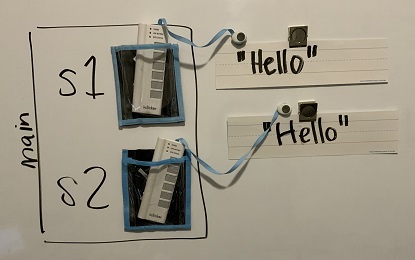
Figure 3: Two strings that are equal with equals but not with ==.¶
Note that you can also create Strings using string literals instead of new, like String s = "Hello". String literals behave a little differently because they are re-used if they already exist instead of creating a new object. But you should not see questions with string literals and == on the AP exam.
Note
Only use == with primitive types like int or to test if two strings (or objects) refer to the same object. Use equals, not ==, with strings to test if they are equal letter by letter.
- s1 == s2 && s1 == s3
- Do s1 and s3 refer to the same object?
- s1 == s2 && s1.equals(s3)
- Yes s2 was set to refer to the same object as s1 and s1 and s3 have the same characters.
- s1 != s2 && s1.equals(s3)
- Did you miss that s2 was set to refer to the same object as s1?
3-7-5: Which of the following is true after the code executes?
String s1 = new String("hi");
String s2 = new String("bye");
String s3 = new String("hi");
s2 = s1;
- s1 == s2 && s1 == s3
- Do s1 and s2 refer to the same object?
- s2.equals(s3) && s1.equals(s3)
- Does s2 have the same characters as s1 or s3?
- s1 != s3 && s1.equals(s3)
- s1 and s3 refer to different string objects but they contain the same characters "hi" in the same order.
3-7-6: Which of the following is true after the code executes?
String s1 = new String("hi");
String s2 = new String("bye");
String s3 = new String("hi");
- s1 == s3 && s1.equals(s3)
- Since s3 uses the new operator it will not refer to the same object as s1.
- s2.equals(s3) && s1.equals(s3)
- Do s2 and s3 have the same characters in the same order?
- !(s1 == s2) && !(s1 == s3)
- All of the variables refer to different objects. But, s1.equals(s3) would be true since they have the same characters in the same order.
3-7-7: Which of the following is true after the code executes?
String s1 = new String("hi");
String s2 = new String("bye");
String s3 = new String("hi");
3.7.3. Comparing with null¶
One common place to use == or != with objects is to compare them to null to see if they really exist. Sometimes short-circuit evaluation is used to avoid an error if the object doesn’t exist. Remember that short-circuit evaluation is used with && in Java meaning that if the first part of the if condition is false, it doesn’t even have to check the second condition and it knows the whole && test is false.
Try the following code to see a NullPointerException (if you don’t see the exception because of the autograding, you can copy it into the pencil icon scratch area to run it without the grader). Since s is null, trying to access indexOf on s throws an NullPointerException. Comment out the first if statement and run the program again. The second if statement avoids the error with shortcircuit evaluation. Because s != null is false, the rest of the Boolean expression is not evaluated. Now, change s to set it to "apple" instead of null in the first line and run the code again to see that the if statements can print out that “apple contains an a”.
The following video shows how the null string reference works in memory.
3.7.4.  Programming Challenge : Tracing Code¶
Programming Challenge : Tracing Code¶
What will the following code print out? Trace through the code by drawing diagrams of what is going on in memory like the figures above, and then show the values of s1, s2, s3, s4 and the output after each line of code. Remember that you can use trace tables to track the values of variables as they change throughout a program. To trace through code, write down a variable in each column in a table and keep track of its value throughout the program as you go through it line by line.
String s1 = null;
String s2 = new String("hi");
String s3 = new String("hi");
String s4 = new String("bye");
if (s1 == null)
{
s1 = s2;
}
if (s1 == s2)
{
System.out.println("s1 and s2 refer to the same object");
}
if (s2 == s3)
{
System.out.println("s2 and s3 refer to the same object");
}
if (s3 == s4)
{
System.out.println("s3 and s4 refer to the same object");
}
if (s1.equals(s2) && s2.equals(s3))
{
System.out.println("s1, s2, s3 are equal");
}
3-7-10: Write your tracing table here that keeps track of s1, s2, s3, s4 and the output.
3.7.5. Summary¶
Often classes have their own equals method, which can be used to determine whether two objects of the class are equivalent.
Two object references are considered aliases when they both reference the same object.
Object reference values can be compared, using
==and!=, to identify aliases.A reference value can be compared with null, using
==or!=, to determine if the reference actually references an object.
3.7.6. AP Practice¶
message == note && message == memo
-
Message does not refer to the same object as memo.
message.equals(note) && message.equals(memo)
-
Message is not the same string as in memo.
message == note && memo.equals(“Practice”)
-
Yes, both if statements in the code above execute changing message to equal note and memo to equal “Practice”.
message != note || message == memo
-
Both of these are false.
message.equals(memo) || memo.equals(note)
-
Both of these are false.
3-7-11: Consider the following code segment.
String message = new String("AP Practice");
String note = new String("AP Practice");
String memo = new String("memo");
int i = 5;
if (message.equals(note) && !message.equals("memo"))
{
message = note;
if (message == note && message.length() > i)
{
i = 3;
memo = message.substring(i);
}
}
Which of the following expressions evaluate to true after the code segment above executes?


